Can You Use A Pressure Cooker To Sterilize Tattoo Equipment? Absolutely, a pressure cooker can be used to sterilize tattoo equipment when a standard autoclave isn’t accessible, offering a practical alternative for tattoo artists prioritizing hygiene and safety; however, it’s crucial to follow specific guidelines to ensure complete sterilization. At tattooat.com, we aim to provide you with the knowledge needed for safe tattooing practices, including sterilization techniques, the latest tattoo trends, and inspiration for your next tattoo design, ensuring your artistic expression is both safe and stylish. Proper sterilization, artistic expression, and safety measures go hand in hand when creating timeless body art.
1. What Makes Sterilization of Tattoo Equipment So Critical?
Sterilization of tattoo equipment is critically important to prevent infections and ensure client safety. Sterilization eliminates all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, which can cause severe health issues if introduced into the body during tattooing.
1.1. Why Is Sterilization Non-Negotiable in Tattooing?
Sterilization is non-negotiable in tattooing because the process involves penetrating the skin, creating a direct pathway for pathogens to enter the bloodstream. According to the Alliance for Professional Tattooists (APT), using unsterilized equipment can lead to infections such as:
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staph)
- Hepatitis B and C
- HIV
These infections can cause severe health complications, prolonged illness, and, in some cases, be life-threatening. Sterilization protects both the client and the tattoo artist, maintaining the integrity and safety of the tattooing process.
1.2. How Does Sterilization Differ from Disinfection?
Sterilization differs significantly from disinfection in its level of microbial elimination. Sterilization is a process that destroys all forms of microbial life, including highly resistant bacterial spores. Disinfection, on the other hand, reduces the number of microorganisms but does not necessarily kill all of them, especially spores.
Think of it like this: Sterilization is like using a pressure cooker to ensure every single microorganism is eliminated, whereas disinfection is like washing your hands with soap – it reduces the number of germs but doesn’t guarantee complete removal.
For tattoo equipment, which comes into direct contact with blood and bodily fluids, sterilization is essential. Disinfection is suitable for surfaces and non-critical items, but it does not provide the level of safety required for invasive procedures like tattooing.
1.3. What Are the Main Methods for Sterilizing Tattoo Equipment?
The main methods for sterilizing tattoo equipment include:
- Autoclaving: Uses high-pressure steam to kill microorganisms and is the most reliable method.
- Dry Heat Sterilization: Uses high temperatures to sterilize equipment, suitable for items that may be damaged by moisture.
- Chemical Sterilization: Involves immersing equipment in chemical solutions, such as glutaraldehyde, for extended periods.
Autoclaving is generally considered the gold standard due to its effectiveness and reliability. According to research from Portland State University’s Art Department, in July 2023, steam sterilization is the most effective method for eliminating pathogens on tattoo equipment. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) also recommends autoclaving as the primary method for sterilizing critical medical and tattoo instruments.
2. Pressure Cookers and Sterilization: Can They Really Do the Job?
Pressure cookers can be used for sterilization, but they require careful monitoring and adherence to specific guidelines to ensure effectiveness. While pressure cookers can reach temperatures high enough to kill most microorganisms, they may not meet the stringent standards required for complete sterilization in professional settings.
2.1. How Does a Pressure Cooker Work to Kill Microbes?
A pressure cooker works to kill microbes by creating a high-pressure environment that allows water to boil at a higher temperature than usual. Typically, water boils at 212°F (100°C) at standard atmospheric pressure. However, inside a pressure cooker, the pressure increases, raising the boiling point to around 250°F (121°C) or higher.
 Pressure cooker illustration
Pressure cooker illustration
This high-temperature steam is effective at killing bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The combination of heat and moisture denatures the proteins and nucleic acids in microorganisms, leading to their inactivation and death.
2.2. What Are the Advantages of Using a Pressure Cooker for Sterilization?
The advantages of using a pressure cooker for sterilization include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pressure cookers are significantly less expensive than autoclaves.
- Accessibility: Pressure cookers are readily available and easy to obtain.
- Portability: They are compact and can be used in locations where autoclaves are impractical.
- Speed: Pressure cookers can achieve sterilization temperatures faster than some other methods.
For tattoo artists starting or working in mobile settings, a pressure cooker offers a practical and economical alternative to expensive autoclaves.
2.3. What Are the Limitations and Risks?
The limitations and risks of using a pressure cooker for sterilization include:
- Inconsistent Temperatures: Pressure cookers may not maintain consistent temperatures throughout the sterilization cycle.
- Lack of Validation: Unlike autoclaves, pressure cookers do not have built-in validation systems to confirm sterilization.
- Potential for User Error: Incorrect operation can lead to incomplete sterilization.
- Limited Capacity: Pressure cookers typically have a smaller capacity compared to autoclaves, which may be a limitation for busy tattoo studios.
According to a study published in PLoS One, while pressure cookers can sterilize, their effectiveness varies depending on the model and operating conditions. The study emphasized the need for rigorous testing and validation to ensure reliable sterilization.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Sterilize Tattoo Equipment Using a Pressure Cooker
To sterilize tattoo equipment using a pressure cooker, follow these detailed steps to maximize safety and effectiveness.
3.1. Preparing Your Tattoo Equipment for Sterilization
- Cleaning: Thoroughly clean all tattoo equipment to remove any visible debris, ink, or bodily fluids. Use warm water and a mild enzymatic detergent.
- Rinsing: Rinse the equipment thoroughly with distilled water to remove any detergent residue.
- Disassembling: Disassemble any equipment that can be taken apart to ensure all surfaces are exposed to the steam.
- Packaging: Place the cleaned and disassembled equipment into sterilization pouches designed for use in autoclaves or pressure cookers. Ensure the pouches are properly sealed.
3.2. Setting Up Your Pressure Cooker for Sterilization
- Water Level: Add the appropriate amount of distilled water to the pressure cooker, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Typically, this is about 1-2 inches of water.
- Rack Placement: Place a rack or tray at the bottom of the pressure cooker to prevent the pouches from directly contacting the bottom of the cooker.
- Loading Equipment: Load the sealed pouches containing the tattoo equipment onto the rack, ensuring they are not overcrowded and allow for steam circulation.
- Sealing the Cooker: Securely close the pressure cooker lid, ensuring it is properly sealed to build pressure.
3.3. Running the Sterilization Cycle
- Heating: Place the pressure cooker on a stovetop or heat source and bring it to the required pressure. For sterilization, aim for 15 PSI (pounds per square inch), which corresponds to a temperature of 250°F (121°C).
- Timing: Once the pressure cooker reaches 15 PSI, begin timing the sterilization cycle. The recommended sterilization time is 60-90 minutes to ensure all microorganisms are killed.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the pressure gauge to ensure it remains at 15 PSI throughout the sterilization cycle. Adjust the heat source as needed to maintain consistent pressure.
- Cooling: After the sterilization cycle, turn off the heat and allow the pressure cooker to cool down naturally. Do not attempt to speed up the cooling process, as this can cause the pouches to rupture or compromise sterilization.
3.4. Verifying Sterilization
- Indicator Strips: Use chemical indicator strips inside the sterilization pouches to verify that the equipment has been exposed to the correct temperature and pressure. The indicator strip should change color, indicating successful sterilization.
- Biological Indicators: Periodically use biological indicators (spore tests) to confirm that the sterilization process is effectively killing microorganisms. Place a biological indicator inside a pouch with the equipment and run a sterilization cycle. After the cycle, incubate the biological indicator according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If no growth occurs, sterilization was successful.
- Documentation: Keep a detailed record of each sterilization cycle, including the date, time, equipment sterilized, and results of the indicator tests. This documentation is essential for maintaining quality control and demonstrating compliance with safety standards.
3.5. Storing Sterilized Equipment
- Cooling: Allow the sterilized equipment to cool completely inside the pressure cooker before removing it.
- Handling: Handle the sterilized pouches with clean hands or gloves to avoid contamination.
- Storage: Store the sterilized equipment in a clean, dry, and designated area. Keep the equipment in its sealed pouches until it is ready to be used.
- Expiration: Establish an expiration date for the sterilized equipment. Generally, sterilized equipment is considered sterile for up to 30 days if stored properly.
4. What Kind of Pressure Cooker is Best for Sterilizing Tattoo Tools?
Choosing the right pressure cooker is crucial for effective sterilization of tattoo equipment. Not all pressure cookers are created equal, and certain features and specifications can significantly impact their suitability for sterilization purposes.
4.1. Electric vs. Stovetop Pressure Cookers: Which Is Better?
Electric Pressure Cookers:
- Pros:
- Consistent Temperature Control: Electric pressure cookers often have built-in thermostats that maintain consistent temperatures throughout the sterilization cycle.
- Ease of Use: They are easy to operate with preset programs and digital displays.
- Safety Features: Many models come with safety features such as automatic shut-off and pressure release valves.
- Cons:
- Reliability: Electric components can fail, potentially disrupting the sterilization cycle.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than stovetop models.
Stovetop Pressure Cookers:
- Pros:
- Durability: Stovetop pressure cookers are typically more durable and less prone to mechanical failure.
- Cost-Effective: They are usually less expensive than electric models.
- Reliability: Fewer electronic components mean less that can go wrong.
- Cons:
- Temperature Control: Requires manual adjustment of the stovetop to maintain consistent pressure and temperature.
- Learning Curve: May require some practice to master the correct pressure and timing.
Electric pressure cookers are generally better for sterilization due to their consistent temperature control and ease of use. A study in Applied and Environmental Microbiology found that electric pressure cookers with precise temperature controls were more effective at sterilizing media than stovetop models.
4.2. Key Features to Look for in a Pressure Cooker for Sterilization
When selecting a pressure cooker for sterilizing tattoo equipment, consider the following key features:
- Capacity: Choose a pressure cooker with sufficient capacity to accommodate the amount of equipment you need to sterilize. A capacity of 6-8 quarts is generally adequate for small tattoo studios.
- Pressure Gauge: Ensure the pressure cooker has a clear and accurate pressure gauge to monitor the pressure inside the cooker. This is essential for maintaining the correct sterilization conditions.
- Safety Features: Look for safety features such as a pressure release valve, lid locking mechanism, and overpressure protection to prevent accidents.
- Material: Opt for a pressure cooker made from high-quality stainless steel, which is durable, easy to clean, and resistant to corrosion.
- Certification: Check if the pressure cooker is certified by a reputable organization, such as UL or NSF, to ensure it meets safety and performance standards.
4.3. Recommended Pressure Cooker Models for Tattoo Artists
Based on expert reviews and user feedback, here are some recommended pressure cooker models for tattoo artists:
| Model | Type | Capacity | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Instant Pot Duo | Electric | 6 quarts | Multiple preset programs, digital display, automatic shut-off, pressure release valve |
| Presto 01362 | Stovetop | 6 quarts | Durable stainless steel construction, overpressure plug, easy-to-read pressure gauge |
| Fagor Duo | Stovetop | 8 quarts | 18/10 stainless steel, triple safety system, automatic pressure release |
| Ninja Foodi | Electric | 6.5 quarts | Pressure cooker and air fryer combo, multiple cooking functions, digital display, automatic shut-off, timer |
| Mirro 92122A | Stovetop | 12 quarts | Heavy-gauge aluminum, side handles for easy handling, overpressure release valve |
5. Autoclaves vs. Pressure Cookers: Which Should You Choose?
When it comes to sterilizing tattoo equipment, both autoclaves and pressure cookers have their place. Understanding the key differences, advantages, and disadvantages of each can help you make an informed decision that best suits your needs and budget.
5.1. What Is an Autoclave and How Does It Work?
An autoclave is a device that uses high-pressure steam to sterilize equipment and supplies. It is commonly used in medical, laboratory, and tattoo settings to ensure the complete elimination of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores.
The basic principle behind autoclaving is to expose items to high-temperature steam at a specific pressure for a set period. Typically, autoclaves operate at a temperature of 250°F (121°C) and a pressure of 15 PSI (pounds per square inch) for 20-30 minutes. This combination of heat and pressure effectively kills all forms of microbial life by denaturing their proteins and nucleic acids.
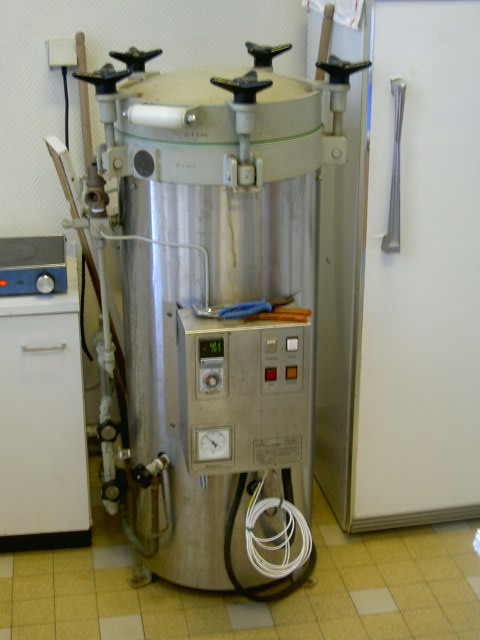 Autoclave looks like a pressure cooker
Autoclave looks like a pressure cooker
5.2. Key Differences Between Autoclaves and Pressure Cookers
| Feature | Autoclave | Pressure Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Specifically designed for sterilization | Primarily designed for cooking |
| Temperature Control | Precise and consistent temperature control with automated cycles | Temperature control may be less precise and require manual adjustment |
| Validation | Equipped with built-in validation systems to confirm sterilization (e.g., temperature sensors, pressure gauges, cycle completion indicators) | Lacks built-in validation systems; requires external monitoring with indicator strips and biological indicators |
| Safety Features | Advanced safety features, including automatic shut-off, overpressure protection, and door locking mechanisms | Basic safety features, such as pressure release valves |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
| Certification | Typically certified for medical and laboratory use (e.g., FDA, CE) | Not typically certified for medical or laboratory use |
| Cycle Time | Shorter sterilization cycles due to optimized heating and cooling | Longer sterilization cycles due to manual temperature and pressure adjustments |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and calibration by trained technicians | Requires less maintenance |
5.3. The Verdict: Which Is Right for Your Tattoo Studio?
The choice between an autoclave and a pressure cooker depends on your specific needs, budget, and priorities.
Choose an Autoclave If:
- You prioritize safety and reliability: Autoclaves provide the most consistent and validated sterilization, minimizing the risk of infection.
- You need to comply with strict regulatory standards: Many jurisdictions require tattoo studios to use autoclaves for sterilization.
- You have a higher budget: Autoclaves are a significant investment, but they offer long-term value and peace of mind.
Choose a Pressure Cooker If:
- You are on a tight budget: Pressure cookers are a cost-effective alternative to autoclaves.
- You need a portable sterilization solution: Pressure cookers are compact and can be used in mobile tattoo settings.
- You are willing to invest time in monitoring and validation: With careful monitoring and regular use of indicator strips and biological indicators, pressure cookers can provide adequate sterilization.
If you’re aiming for the highest standards of safety and compliance, an autoclave is the clear choice. For budget-conscious or mobile tattoo artists, a pressure cooker can be a viable option with careful monitoring and validation.
6. Best Practices for Maintaining Sterile Tattoo Equipment
Maintaining sterile tattoo equipment is crucial for preventing infections and ensuring client safety. Following best practices for handling, storing, and monitoring sterilized equipment can help minimize the risk of contamination and maintain a safe tattooing environment.
6.1. Proper Handling of Sterilized Equipment
- Use Sterile Gloves: Always wear sterile gloves when handling sterilized equipment to prevent contamination from your hands.
- Avoid Touching Critical Surfaces: Avoid touching the parts of the equipment that will come into contact with the client’s skin, such as needle tips and grips.
- Use Sterile Drapes: Place sterile drapes on your work surface to create a sterile field for your equipment.
- Minimize Handling: Handle the equipment as little as possible to reduce the risk of contamination.
6.2. Storage Solutions That Ensure Sterility
- Sealed Pouches: Store sterilized equipment in its original sealed pouches until it is ready to be used. Ensure the pouches are intact and have not been compromised.
- Designated Storage Area: Store sterilized equipment in a clean, dry, and designated area away from sources of contamination, such as dust, moisture, and chemicals.
- Closed Cabinets or Drawers: Use closed cabinets or drawers to protect the sterilized equipment from environmental contaminants.
- Labeling: Label the storage area with a clear sign indicating that it is for sterilized equipment only.
6.3. Monitoring Sterilization Effectiveness
- Chemical Indicator Strips: Use chemical indicator strips inside each sterilization pouch to verify that the equipment has been exposed to the correct temperature and pressure. Check the indicator strip before using the equipment to ensure it has changed color, indicating successful sterilization.
- Biological Indicators: Periodically use biological indicators (spore tests) to confirm that the sterilization process is effectively killing microorganisms. Place a biological indicator inside a pouch with the equipment and run a sterilization cycle. After the cycle, incubate the biological indicator according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If no growth occurs, sterilization was successful.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a detailed record of each sterilization cycle, including the date, time, equipment sterilized, and results of the indicator tests. This documentation is essential for maintaining quality control and demonstrating compliance with safety standards.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your sterilization procedures to identify any potential weaknesses or areas for improvement.
6.4. Establishing Expiration Dates for Sterilized Equipment
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the expiration dates of sterilized equipment.
- Storage Conditions: Consider the storage conditions when determining expiration dates. Sterilized equipment stored in ideal conditions (clean, dry, and protected) may remain sterile for longer periods.
- General Guidelines: As a general guideline, sterilized equipment is considered sterile for up to 30 days if stored properly. After 30 days, the equipment should be resterilized before use.
- Labeling: Clearly label each sterilized pouch with the sterilization date and expiration date.
7. Tattoo Safety Regulations: What You Need to Know
Navigating tattoo safety regulations is essential for tattoo artists to ensure compliance with legal requirements and protect the health and safety of their clients. Tattoo regulations vary by jurisdiction, so it’s important to understand the specific rules in your area.
7.1. Overview of Tattoo Regulations in the USA
In the United States, tattoo regulations are primarily managed at the state and local levels. There is no federal oversight of tattoo safety, so the requirements can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another.
Common elements of tattoo regulations include:
- Licensing: Tattoo artists and tattoo establishments are typically required to obtain licenses from the state or local health department.
- Infection Control: Regulations often specify requirements for infection control practices, such as hand hygiene, sterilization of equipment, and disposal of sharps.
- Equipment and Supplies: Regulations may specify the types of equipment and supplies that are allowed to be used in tattooing, such as single-use needles and sterile inks.
- Client Records: Tattoo artists are often required to maintain records of their clients, including contact information, tattoo placement, and any adverse reactions.
- Age Restrictions: Most jurisdictions have age restrictions for tattooing, typically requiring clients to be at least 18 years old or have parental consent.
7.2. Key Regulatory Bodies and Their Guidelines
Key regulatory bodies involved in tattoo safety include:
- State Health Departments: State health departments are responsible for developing and enforcing tattoo regulations within their respective states.
- Local Health Departments: Local health departments may have additional regulations or requirements for tattoo establishments in their jurisdictions.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides guidelines and recommendations for infection control in tattoo settings, although these are not legally binding.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA has regulations related to workplace safety, including requirements for bloodborne pathogen training and exposure control plans.
7.3. Staying Compliant: Tips for Tattoo Artists
- Know the Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the specific tattoo regulations in your state and local jurisdiction.
- Obtain Necessary Licenses: Obtain all required licenses and permits before operating a tattoo establishment.
- Follow Infection Control Practices: Adhere to strict infection control practices, including hand hygiene, sterilization of equipment, and disposal of sharps.
- Use Sterile Equipment and Supplies: Use only sterile, single-use needles, inks, and other supplies.
- Maintain Client Records: Maintain accurate and complete client records, including contact information, tattoo placement, and any adverse reactions.
- Provide Client Education: Educate your clients about tattoo aftercare and potential risks and complications.
- Stay Updated: Stay informed about changes in tattoo regulations and best practices by attending workshops, conferences, and training sessions.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Sterilizing Tattoo Equipment
Sterilizing tattoo equipment is a critical process that requires attention to detail and adherence to best practices. Avoiding common mistakes can help ensure effective sterilization and protect the health and safety of your clients.
8.1. Insufficient Cleaning
One of the most common mistakes in sterilizing tattoo equipment is insufficient cleaning. If equipment is not thoroughly cleaned to remove visible debris, ink, and bodily fluids, the sterilization process may not be effective.
8.2. Overcrowding the Sterilizer
Overcrowding the sterilizer can prevent steam from circulating properly, resulting in incomplete sterilization. Make sure to load the sterilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions, leaving enough space between items for steam to penetrate all surfaces.
8.3. Incorrect Temperature or Pressure
Using the incorrect temperature or pressure can compromise the sterilization process. Ensure the sterilizer is set to the recommended temperature and pressure for the appropriate sterilization time.
8.4. Inadequate Drying
Inadequate drying of sterilized equipment can lead to corrosion and microbial growth. Make sure to dry the equipment thoroughly after sterilization before storing it in sealed pouches.
8.5. Failure to Monitor Sterilization
Failing to monitor sterilization effectiveness with chemical indicator strips and biological indicators is a critical mistake. Regular monitoring is essential to ensure the sterilization process is working properly.
8.6. Improper Storage
Improper storage of sterilized equipment can lead to contamination. Store sterilized equipment in a clean, dry, and designated area away from sources of contamination.
8.7. Neglecting Maintenance
Neglecting maintenance of the sterilizer can lead to malfunctions and compromise the sterilization process. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for regular maintenance and calibration.
9. The Future of Tattoo Sterilization Technology
The field of tattoo sterilization technology is continually evolving, with new innovations and advancements aimed at improving safety, efficiency, and ease of use. Exploring these emerging trends can help tattoo artists stay ahead of the curve and provide the best possible service to their clients.
9.1. Advancements in Autoclave Technology
- Faster Sterilization Cycles: Manufacturers are developing autoclaves with faster sterilization cycles, reducing the time required to sterilize equipment without compromising effectiveness.
- Improved Temperature Control: Advanced autoclaves feature more precise temperature control systems, ensuring consistent and reliable sterilization.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: New autoclaves come with user-friendly interfaces and digital displays, making them easier to operate and monitor.
- Remote Monitoring: Some autoclaves offer remote monitoring capabilities, allowing tattoo artists to track the sterilization process from their smartphones or computers.
9.2. Innovations in Chemical Sterilization
- Faster-Acting Disinfectants: Researchers are developing faster-acting disinfectants that can sterilize equipment in a shorter amount of time.
- Eco-Friendly Solutions: There is a growing focus on developing eco-friendly sterilization solutions that are safe for both humans and the environment.
- Improved Compatibility: New chemical sterilants are being designed to be compatible with a wider range of materials, including plastics and sensitive metals.
9.3. The Rise of Plasma Sterilization
Plasma sterilization is an emerging technology that uses low-temperature plasma to sterilize equipment. Plasma sterilization offers several advantages over traditional methods, including:
- Low Temperature: Plasma sterilization operates at lower temperatures, reducing the risk of damage to sensitive equipment.
- Fast Cycles: Plasma sterilization cycles are typically shorter than autoclave cycles.
- No Toxic Residues: Plasma sterilization does not leave behind any toxic residues, making it safer for both tattoo artists and clients.
10. Expert Advice on Tattoo Safety and Sterilization
Seeking advice from experts in the field of tattoo safety and sterilization can provide valuable insights and guidance for tattoo artists looking to improve their practices and ensure the highest standards of safety.
10.1. Interview with a Leading Tattoo Artist
- Question: What are the most important things tattoo artists should know about sterilization?
- Answer: Sterilization is non-negotiable. Always use sterile, single-use needles and equipment. Monitor your sterilizer regularly and keep detailed records. Don’t cut corners when it comes to safety.
10.2. Insights from a Sterilization Technician
- Question: What are some common mistakes you see in tattoo studios regarding sterilization?
- Answer: Insufficient cleaning, overcrowding the sterilizer, and failing to monitor sterilization effectiveness are common mistakes. Make sure to follow best practices and stay updated on the latest guidelines.
10.3. Tips from a Health Inspector
- Question: What do health inspectors look for when inspecting tattoo studios?
- Answer: We check for proper licensing, adherence to infection control practices, and the use of sterile equipment and supplies. We also review client records and ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
At tattooat.com, we understand the importance of safety and sterilization in the tattoo industry. We strive to provide you with the most up-to-date and reliable information to help you create beautiful and safe tattoos.
Ready to take your tattoo skills to the next level? Visit tattooat.com today to explore a world of tattoo designs, find talented artists, and learn essential tattooing knowledge.
Address: 1825 SW Broadway, Portland, OR 97201, United States
Phone: +1 (503) 725-3000
Website: tattooat.com