Did The Incas Have Tattoos? Yes, the practice of tattooing existed in the Andean region long before the Inca Empire, with evidence suggesting the Incas continued, and perhaps adapted, these traditions. Tattooat.com is your premier online destination for discovering the rich history and artistry of tattoos, providing insights into ancient practices and connecting you with contemporary tattoo artists inspired by these traditions. Discover designs and artists that resonate with your personal style, honoring the legacy of ancient cultures.
1. What Evidence Suggests the Incas Practiced Tattooing?
While direct evidence of Inca tattoos is scarce, the prevalence of tattooing in pre-Inca cultures of coastal Peru strongly implies that the practice continued, possibly with adaptations, into the Inca period. Archaeological discoveries of mummies with tattoos, like those of the Chimú and Moche cultures, showcase the intricate designs and techniques used in the region prior to Inca rule.
- Mummy Discoveries: Hundreds of mummies bearing tattoos have been unearthed in the coastal valleys of Peru, illustrating that the art form was well-established long before the rise of the Inca Empire (Allison, 1996).
- Cultural Continuity: Given the Inca’s tendency to absorb and adapt cultural practices from conquered peoples, it’s probable that they incorporated tattooing into their own customs. The Chimú, known as the most heavily tattooed of Peru’s ancient cultures, were eventually conquered by the Incas (Topic, 1990).
- Symbolic Raiment: Tattoos may have served as a “double-sided raiment,” concealing and projecting personal power and identity among both the living and the dead. This concept aligns with the Inca worldview, where symbols and status were paramount (Anzieu, 1989).
 Chimú mummies with zoomorphic and geometric tattooing, ca. 1200 A.D featuring fish and harpoon points
Chimú mummies with zoomorphic and geometric tattooing, ca. 1200 A.D featuring fish and harpoon points
2. Which Pre-Inca Cultures Practiced Tattooing in Peru?
Several cultures in pre-Inca Peru were known for their elaborate tattooing traditions, with the Chimú and Moche standing out as the most prominent. Discoveries of tattooed mummies and artifacts depicting body art provide valuable insights into the artistry and significance of these ancient practices.
- Chimú Culture: The Chimú (1100-1470 A.D.) were renowned for their extensive and intricate tattoos. These designs, often featuring stylized marine and terrestrial fauna, abstract geometric patterns, and anthropomorphic deities, were found on living flesh and carved into burial objects (Allison et al., 1981).
- Moche Culture: The Moche (50-800 A.D.) also practiced tattooing, as evidenced by mummified remains discovered at sites like El Brujo. The “Lady of Cao,” an elite Moche woman, was found with intricate tattoos of supernatural creatures and geometric designs covering her forearms, hands, and knuckles (Williams, 2006).
- Other Cultures: Other pre-Inca cultures, including the Paracas, Nasca, and Wari-Tiwanaku, also engaged in ritualistic practices, including the tradition of human heads for ritual use (Proulx, 2001).
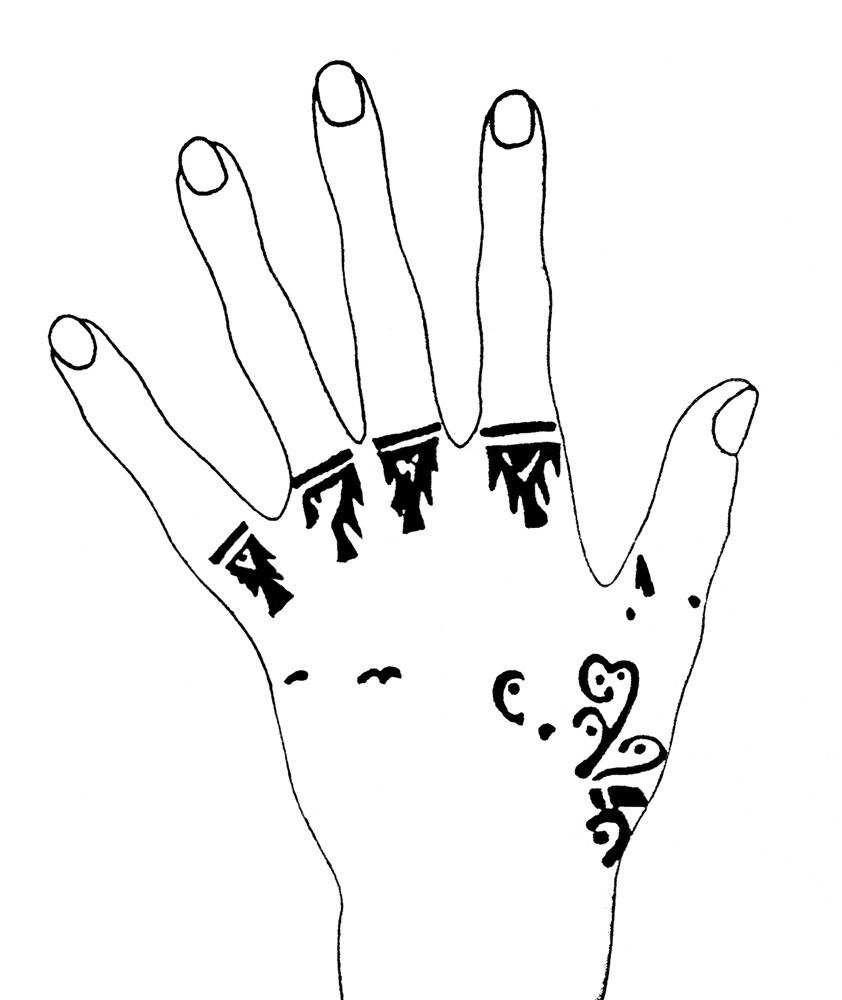
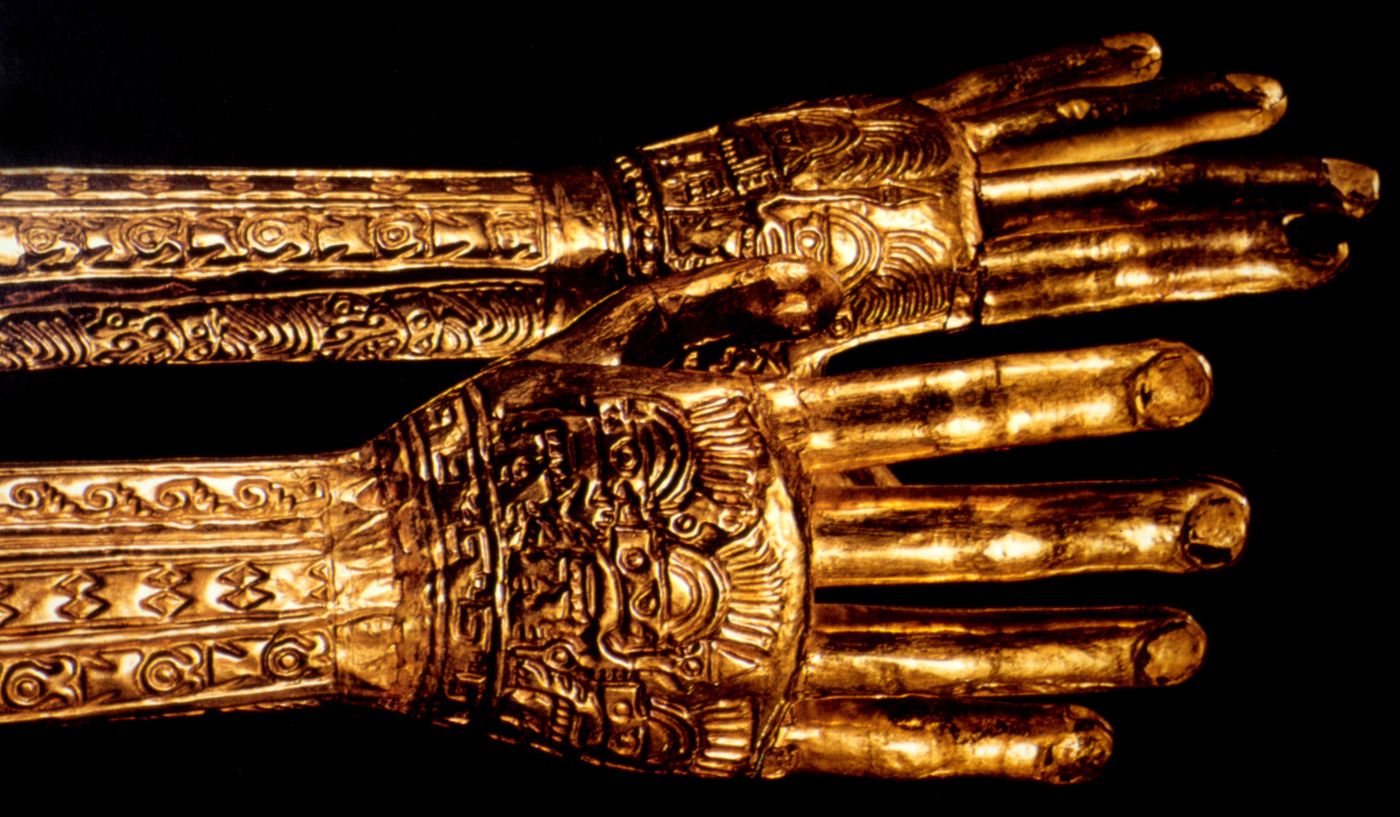 Moche gold hands showcasing intricate tattoo designs meant to carry the tattoos into eternity
Moche gold hands showcasing intricate tattoo designs meant to carry the tattoos into eternity
3. What Designs Were Common in Ancient Peruvian Tattoos?
Ancient Peruvian tattoos featured a diverse array of designs, often reflecting the natural world, religious beliefs, and social status of the individuals who wore them. Stylized marine and terrestrial fauna, geometric patterns, and depictions of deities were among the most popular motifs.
- Marine and Terrestrial Fauna: Fish, lizards, birds, and other animals were common motifs, reflecting the close relationship between the people and their environment. For example, the remains of Chimú mummies have motifs that include lizards, ocean waves, and harpoon points (Allison et al., 1981).
- Geometric Patterns: Abstract geometric designs, such as ocean waves, mountains, and V-shaped markings, may have represented features of the surrounding landscape or conveyed symbolic meanings. V-shaped chest markings, found in the Moche ceramics, depict two male captives wearing a series of markings that include serpentine elements (Donnan and McClelland, 1999).
- Anthropomorphic Deities: Depictions of anthropomorphic deities suggest a spiritual connection. The Lady of Cao’s tattoos featured spiders and birds, possibly reflecting her status or religious role in society (Williams, 2006).
4. What Materials Were Used to Create Tattoos in Ancient Peru?
Ancient Peruvian tattoo artists utilized a variety of natural materials to create their indelible designs, with the black dye derived from the genipap fruit being a prominent choice. These materials and techniques reflect the ingenuity and resourcefulness of these early tattoo practitioners.
- Genipap Fruit: The juice of the green, immature genipap fruit was commonly used as a black body paint and tattoo pigment. Archaeological excavations in the Huaura Valley revealed mummies clutching dried-up genipap fruit in their palms, indicating its significance in funerary practices (Knol, 1990).
- Needles: Tattoo pigments were applied with fine needles made from fishbone, parrot quill, or spiny conch. These tools allowed for precise application of the designs (Allison et al., 1981).
- Soot Carbon and Charcoal: Studies of a Chiribaya Alta mummy revealed the use of two different organic pigments: soot carbon for decorative tattoos and charcoal from pyrolyzed plant material for therapeutic tattoos (Pabst et al., 2010).
 Tattoos found on the neck of a female Chiribaya Alta mummy, 1000 A.D.
Tattoos found on the neck of a female Chiribaya Alta mummy, 1000 A.D.
5. What Was the Tattooing Process Like in Ancient Peru?
The tattooing process in ancient Peru involved hand-poking and skin-stitching techniques, similar to the “facial embroidery” practiced by the Inuit. This meticulous and labor-intensive method required skilled artisans who possessed extensive knowledge of anatomy and artistic design.
- Hand-Poking and Skin-Stitching: Tattoo artists used fine needles to puncture the skin and insert the pigment. This process may have been similar to the facial embroidery practiced by the Inuit, where designs were stitched into the skin (Allison et al., 1981).
- Skilled Artisans: The creation of intricate tattoo designs required highly skilled artisans with a deep understanding of anatomy and artistic design. These individuals likely held a position of prestige in their communities and were compensated for their expertise.
- Possible Gender Roles: It’s been suggested that women were the primary tattoo artists, given their expertise in working with animal skins and hides. Their knowledge would have facilitated the precision needed to pierce the human epidermis with complex motifs.
6. What Role Did Tattooing Play in Ancient Peruvian Society?
Tattooing in ancient Peru held significant cultural, social, and religious importance. It served as a means of expressing identity, conveying status, and connecting with the spiritual realm.
- Identity and Status: Tattoos served as a way to establish identity, similar to a name, and reconstruct personhood. The designs worn on the skin could indicate an individual’s social status, lineage, or accomplishments (Anzieu, 1989).
- Spiritual Significance: Tattoos may have acted as magical mediators between the living world and the afterlife. By reinforcing the skin and its boundaries, these markings may have been thought to work apotropaically in the afterlife (Allison, 1996).
- Therapeutic Purposes: Some tattoos may have had therapeutic functions. The alignment of tattoos on a Chiribaya Alta mummy’s neck with acupuncture points suggests that they were used to relieve discomfort (Pabst et al., 2010).
7. How Did the Incas Influence Tattooing in the Andean Region?
While concrete evidence of Inca-specific tattoo designs is lacking, the Inca Empire’s influence on the Andean region likely extended to the realm of body art. The Incas were known for assimilating and adapting the customs and traditions of the cultures they conquered, potentially leading to a fusion of artistic styles and symbolic meanings.
- Cultural Assimilation: The Incas often adopted the cultural practices of the peoples they conquered, integrating them into their own society. This suggests that tattooing, which was already prevalent in the region, may have been incorporated into Inca customs.
- Symbolic Adaptation: The Incas may have adapted existing tattoo designs to align with their own religious beliefs and social hierarchy. This could have resulted in the creation of new motifs or the modification of existing ones to reflect Inca ideology.
- Elite Practices: Tattooing may have been reserved for the Inca elite, serving as a marker of status and power. The most affluent or aristocratic individuals could afford tattoos, as skin artisans received high wages for their artistry.
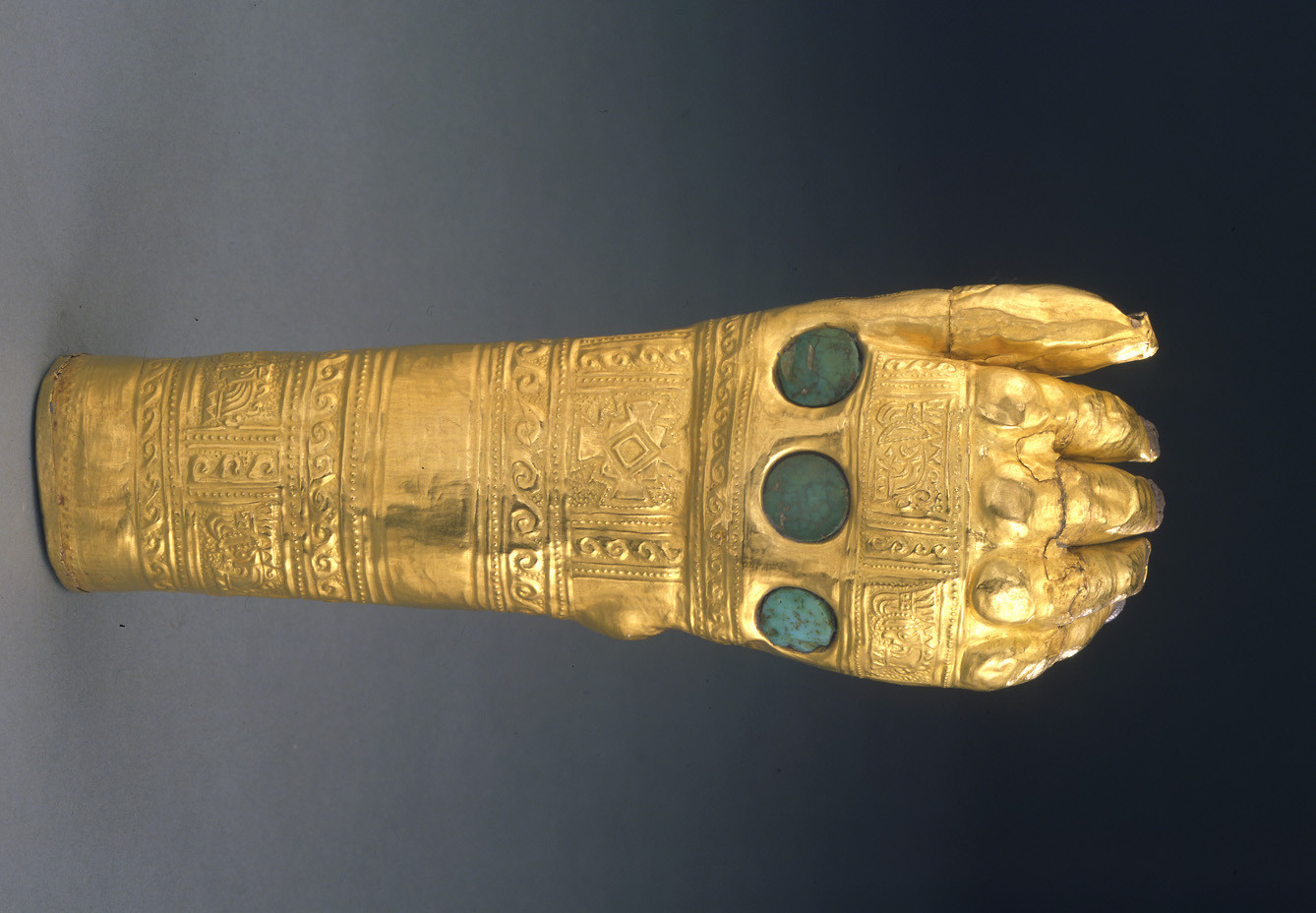 Hammered gold hand with intricate tattoo motifs from the Lambayeque (Sicán) culture, 800-1370 A.D.
Hammered gold hand with intricate tattoo motifs from the Lambayeque (Sicán) culture, 800-1370 A.D.
8. Did Tattooing Have Medicinal Purposes in Ancient Andean Cultures?
Yes, evidence suggests that tattooing served medicinal purposes in ancient Andean cultures. The discovery of a mummy with tattoos aligned with acupuncture points indicates that these markings were used therapeutically.
- Acupuncture Alignment: Tattoos found on the neck of a female Chiribaya Alta mummy were aligned with acupuncture points used today to relieve neck and head discomfort (Pabst et al., 2010).
- Therapeutic Pigments: The mummy was tattooed with two different organic pigments: soot carbon for decorative tattoos and charcoal from pyrolyzed plant material for therapeutic tattoos (Pabst et al., 2010).
- Holistic Healing: The use of tattoos for medicinal purposes reflects a holistic approach to healing, where the physical and spiritual aspects of well-being were interconnected.
9. How Does Ancient Andean Tattooing Compare to Other Tattoo Traditions Around the World?
Ancient Andean tattooing shares similarities with other tattoo traditions worldwide, particularly in its use of natural pigments, hand-poking techniques, and symbolic designs. However, it also possesses unique characteristics that reflect the specific cultural and environmental context of the Andean region.
- Natural Pigments: Like many ancient cultures, Andean tattoo artists relied on natural pigments derived from plants, minerals, and other organic sources. This practice is common across diverse tattoo traditions, from the Maori of New Zealand to the tribes of Borneo.
- Hand-Poking Techniques: The hand-poking and skin-stitching techniques used in ancient Peru are similar to methods employed by indigenous cultures around the world. This manual process allows for precise control and artistic expression.
- Symbolic Designs: The use of symbolic designs to convey identity, status, and spiritual beliefs is a universal feature of tattoo traditions. However, the specific symbols and motifs vary depending on the cultural context.
10. How Can I Learn More About Ancient Andean Tattooing and Find Inspiration for My Own Tattoo?
To delve deeper into the world of ancient Andean tattooing, tattooat.com offers a wealth of resources and inspiration. Explore our extensive collection of tattoo designs, connect with talented artists specializing in cultural and historical styles, and learn about the rich history and symbolism behind these ancient practices.
- Explore Designs: Browse our extensive collection of tattoo designs inspired by ancient Andean art. Discover motifs, patterns, and symbols that resonate with your personal style and interests.
- Connect with Artists: Find talented tattoo artists specializing in cultural and historical styles. Connect with artists who can bring the beauty and meaning of ancient Andean tattooing to life on your skin.
- Learn the History: Read in-depth articles and guides on tattooat.com to learn about the history, symbolism, and techniques of ancient Andean tattooing. Understand the cultural context and significance of these ancient practices.
 Moche woman’s arm tattooing from Pacatnamu, showcasing the Mochica style and anthropomorphic creatures
Moche woman’s arm tattooing from Pacatnamu, showcasing the Mochica style and anthropomorphic creatures
11. What Are Some Contemporary Tattoo Styles Inspired by Ancient Andean Art?
Several contemporary tattoo styles draw inspiration from ancient Andean art, blending traditional motifs with modern techniques and aesthetics. These styles offer a unique way to honor the legacy of ancient cultures and express your personal connection to the Andean region.
- Geometric Abstraction: This style incorporates the geometric patterns and abstract designs found in ancient Andean textiles and ceramics. Tattoo artists use precise lines, shapes, and shading to create visually stunning and symbolic compositions.
- Mythological Realism: This style depicts mythological creatures, deities, and ancestral figures from Andean folklore. Tattoo artists employ realistic techniques to bring these figures to life on the skin, capturing their power and mystique.
- Modern Interpretations: This style reinterprets ancient Andean motifs through a contemporary lens. Tattoo artists experiment with new colors, techniques, and compositions to create unique and innovative designs that pay homage to the past while embracing the future.
12. Where Can I Find Reputable Tattoo Artists in the USA Who Specialize in Andean-Inspired Tattoos?
Finding a reputable tattoo artist specializing in Andean-inspired tattoos in the USA requires careful research and consideration. Tattooat.com can help you connect with talented artists who possess the knowledge, skills, and cultural sensitivity to create authentic and meaningful designs.
- Online Directories: Use online directories like tattooat.com to search for tattoo artists in your area who specialize in cultural or historical styles. Read reviews and testimonials to get a sense of their reputation and expertise.
- Social Media: Explore social media platforms like Instagram and Pinterest to find tattoo artists who showcase Andean-inspired designs. Look for artists who demonstrate a deep understanding of the culture and symbolism behind the tattoos.
- Tattoo Conventions: Attend tattoo conventions and festivals in the USA to meet artists from around the country and see their work in person. This is a great opportunity to connect with artists who specialize in cultural and historical styles.
13. How Can I Ensure My Andean-Inspired Tattoo Is Culturally Sensitive and Respectful?
Ensuring your Andean-inspired tattoo is culturally sensitive and respectful requires careful research, consultation, and collaboration with knowledgeable artists. By taking the time to understand the cultural context and significance of your chosen designs, you can create a tattoo that honors the traditions of the Andean region.
- Research the Culture: Before getting an Andean-inspired tattoo, take the time to research the culture and history behind the designs you’re interested in. Learn about the symbolism, meaning, and significance of the motifs you’re considering.
- Consult with Experts: Consult with cultural experts or historians who specialize in Andean art and culture. They can provide valuable insights into the proper use and interpretation of traditional designs.
- Collaborate with Artists: Work closely with a tattoo artist who is knowledgeable about Andean culture and sensitive to its traditions. Collaborate on the design to ensure that it is both aesthetically pleasing and culturally appropriate.
14. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Tattooing in Ancient Andean Cultures?
Several misconceptions surround tattooing in ancient Andean cultures, often stemming from a lack of historical context or a misunderstanding of the cultural practices. By dispelling these myths, we can gain a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the role and significance of tattooing in these societies.
- Tattoos Were Only for Criminals: This is a common misconception about tattooing in many ancient cultures. In ancient Peru, tattoos were worn by people from all walks of life, including elites, warriors, and religious figures.
- Tattoos Were Painful and Unhygienic: While tattooing undoubtedly involved some level of discomfort, ancient Andean cultures developed techniques and materials to minimize pain and prevent infection. The use of natural pigments and fine needles suggests a sophisticated understanding of hygiene and wound care.
- Tattoos Were Primitive and Unsophisticated: The intricate designs and symbolic meanings found in ancient Andean tattoos demonstrate a high level of artistic skill and cultural complexity. These tattoos were far from primitive; they were a sophisticated form of self-expression and cultural communication.
15. How Has Tattooing Evolved in Peru Since the Inca Era?
Tattooing in Peru has undergone significant transformations since the Inca era, influenced by colonization, globalization, and changing social attitudes. While traditional practices have faded, contemporary tattoo artists are reviving and reinterpreting ancient motifs, blending them with modern styles and techniques.
- Colonial Influence: The arrival of the Spanish colonizers in the 16th century led to the suppression of many indigenous cultural practices, including tattooing. The Catholic Church viewed tattooing as a pagan ritual and discouraged its practice.
- Modern Revival: In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in traditional Peruvian art and culture, including tattooing. Contemporary tattoo artists are drawing inspiration from ancient motifs and techniques, creating new designs that honor the country’s rich heritage.
- Fusion of Styles: Modern Peruvian tattooing often blends traditional Andean motifs with contemporary styles, such as realism, geometric abstraction, and watercolor. This fusion creates unique and innovative designs that appeal to a diverse clientele.
16. Where Can I See Examples of Ancient Andean Tattoos on Display?
Unfortunately, due to the delicate nature of mummified remains, opportunities to view ancient Andean tattoos on display are limited. However, several museums and cultural institutions around the world house collections of artifacts and textiles that depict tattoo designs and provide valuable insights into the art form.
- Museo Oro del Perú (Lima, Peru): This museum houses a collection of gold artifacts, including hammered gold hands with intricate tattoo motifs. These artifacts provide a glimpse into the artistic styles and symbolic meanings of ancient Andean tattoos.
- Dumbarton Oaks (Washington, D.C., USA): This research library and museum has a collection of pre-Columbian art, including Lambayeque gold hands with tattoo motifs and Moche bone spatulas with carved designs.
- British Museum (London, UK): The British Museum’s collection includes Moche bone spatulas with incised designs that likely represent tattoos of anthropomorphic deities, zoomorphs, war clubs, and goblets of blood.
17. What Are Some Ethical Considerations When Getting a Tattoo Inspired by Ancient Cultures?
When getting a tattoo inspired by ancient cultures, it’s crucial to consider the ethical implications and ensure that your design is respectful and meaningful. Avoid appropriating symbols or motifs without understanding their cultural context, and always seek guidance from knowledgeable sources.
- Avoid Appropriation: Be mindful of cultural appropriation, which is the act of taking or using elements of a culture that is not your own without understanding or respecting its significance. Avoid using symbols or motifs simply because they look “cool” or “exotic.”
- Seek Permission: If you’re interested in using a design that is considered sacred or restricted within a particular culture, seek permission from community leaders or cultural representatives. Respect their wishes if they decline to grant permission.
- Educate Yourself: Take the time to educate yourself about the culture and history behind your chosen design. Understand its symbolism, meaning, and significance within its original context.
18. How Can I Support Indigenous Artists and Communities When Getting an Andean-Inspired Tattoo?
Supporting indigenous artists and communities is a vital part of ensuring that your Andean-inspired tattoo is both meaningful and ethical. By choosing to work with indigenous artists or donating to indigenous organizations, you can help preserve and promote traditional art forms and cultural practices.
- Work with Indigenous Artists: Seek out indigenous tattoo artists who specialize in traditional Andean designs. By working with these artists, you can support their livelihoods and ensure that your tattoo is created with cultural authenticity and respect.
- Donate to Indigenous Organizations: Donate to organizations that support indigenous artists and communities in the Andean region. These organizations provide funding, resources, and training to help preserve and promote traditional art forms and cultural practices.
- Promote Indigenous Art: Share your Andean-inspired tattoo on social media and credit the artist or culture that inspired it. Use your platform to promote indigenous art and raise awareness about the importance of cultural preservation.
19. What Is the Future of Tattooing in Peru and the Andean Region?
The future of tattooing in Peru and the Andean region is bright, with a growing interest in traditional art forms and a new generation of artists who are committed to preserving and promoting their cultural heritage. As tattooing becomes more mainstream, it has the potential to serve as a powerful tool for cultural expression, identity formation, and social change.
- Cultural Preservation: Tattooing can play a vital role in preserving and promoting traditional Andean art forms and cultural practices. By incorporating ancient motifs and techniques into contemporary designs, tattoo artists can help keep these traditions alive for future generations.
- Identity Formation: Tattoos can serve as a powerful way for people to connect with their cultural heritage and express their personal identity. For indigenous communities in the Andean region, tattoos can be a source of pride, resilience, and cultural resistance.
- Social Change: Tattooing can also be used to challenge social norms, promote social justice, and raise awareness about important issues. By using their bodies as canvases, individuals can express their beliefs, challenge stereotypes, and advocate for change.
20. How Can Tattooat.com Help Me on My Tattoo Journey?
Tattooat.com is your ultimate guide to the world of tattoos, offering a wealth of resources, inspiration, and connections to help you on your tattoo journey. Whether you’re seeking information about ancient tattooing traditions, searching for a talented artist, or simply looking for inspiration, tattooat.com has everything you need.
- Extensive Design Gallery: Browse our extensive gallery of tattoo designs, featuring a wide range of styles, motifs, and cultural influences. Find inspiration for your next tattoo and discover new artists and techniques.
- Artist Directory: Connect with talented tattoo artists from around the world who specialize in various styles, including cultural and historical designs. Read reviews, view portfolios, and book consultations to find the perfect artist for your needs.
- Informative Articles: Read in-depth articles and guides on all aspects of tattooing, from its history and cultural significance to the latest techniques and trends. Educate yourself about the art of tattooing and make informed decisions about your own tattoo journey.
Ready to explore the fascinating world of tattoos? Visit tattooat.com today and discover the designs, artists, and knowledge you need to embark on your own unique tattoo adventure. Let us help you find the perfect tattoo to express your individuality, honor your heritage, and connect with the rich tapestry of human culture. Contact us at Address: 1825 SW Broadway, Portland, OR 97201, United States or Phone: +1 (503) 725-3000.
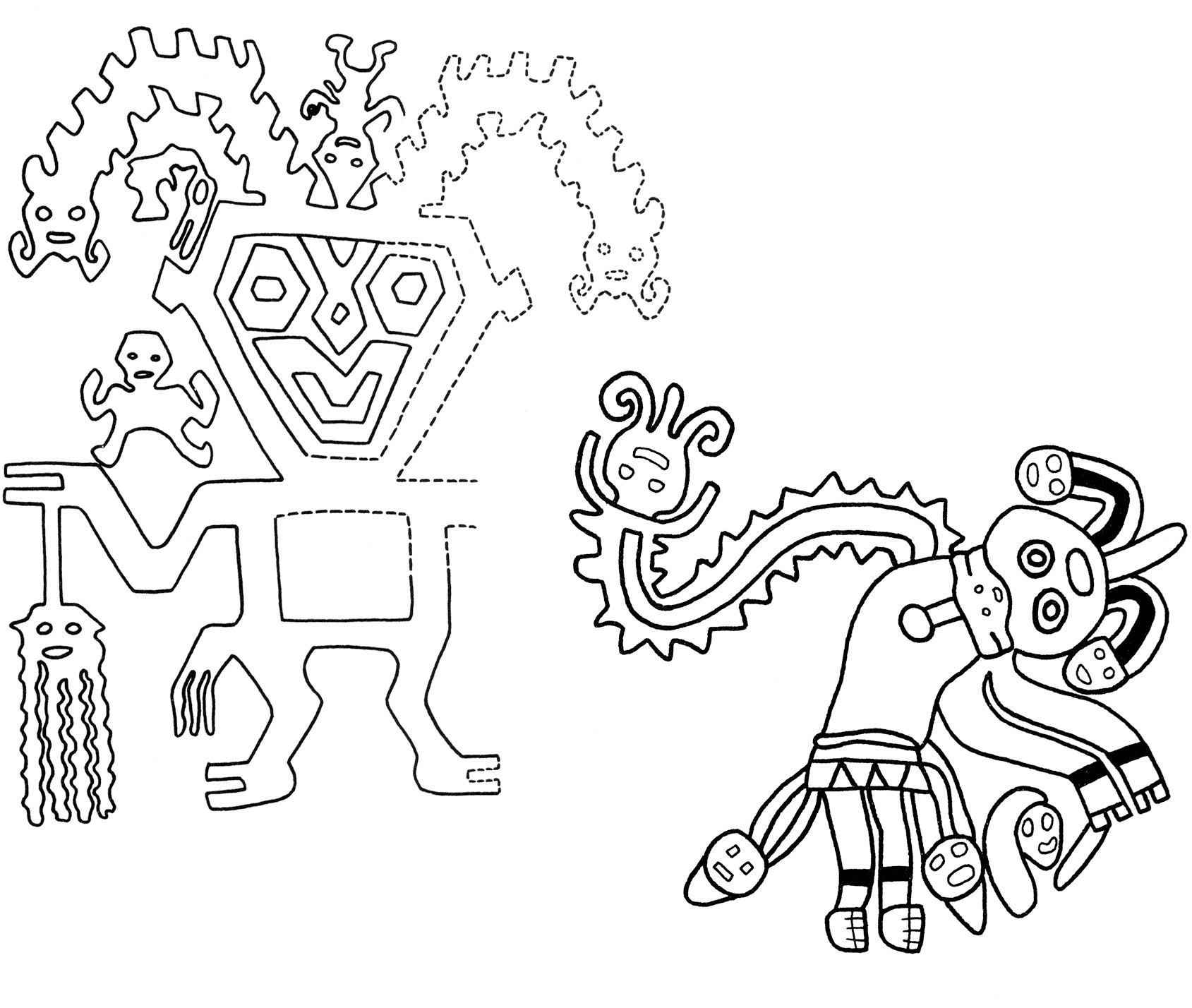 Paracas burial textile designs with trophy head and centipede theme, showcasing the intricate patterns
Paracas burial textile designs with trophy head and centipede theme, showcasing the intricate patterns
FAQ: Did The Incas Have Tattoos?
1. Did the Incas themselves practice tattooing?
While direct evidence is limited, the prevalence of tattooing in pre-Inca cultures suggests the Incas likely adopted and adapted the practice, integrating it into their own customs.
2. What pre-Inca cultures are known for their tattooing?
The Chimú and Moche cultures were particularly renowned for their elaborate tattooing traditions, as evidenced by mummified remains and artifacts.
3. What kind of designs were used in ancient Peruvian tattoos?
Common designs included stylized animals, geometric patterns, and representations of deities, reflecting the natural world and religious beliefs.
4. What materials did ancient Peruvians use for tattoos?
They primarily used natural materials like the juice of the genipap fruit for black dye and fine needles made from fishbone or quills.
5. How was tattooing done in ancient Peru?
The process involved hand-poking and skin-stitching techniques, similar to facial embroidery, performed by skilled artisans.
6. What role did tattoos play in ancient Peruvian society?
Tattoos served as markers of identity, status, and spiritual connection, often acting as mediators between the living world and the afterlife.
7. How did the Inca civilization affect tattooing practices in the region?
The Incas’ tendency to assimilate cultural practices suggests they likely incorporated tattooing, potentially adapting designs to fit their own ideology.
8. Were tattoos used for medicinal purposes in ancient Andean cultures?
Yes, tattoos were sometimes aligned with acupuncture points, indicating a therapeutic function to relieve discomfort.
9. How does Andean tattooing compare to other global tattoo traditions?
Andean tattooing shares similarities in its use of natural pigments and hand-poking techniques, but has unique designs reflecting its specific cultural context.
10. How can I find inspiration for a tattoo based on ancient Andean art?
Explore online resources like tattooat.com for design ideas, connect with artists specializing in cultural styles, and research the history and symbolism behind ancient motifs.
